Strokes are one of the most important contemporary problems medicine. It is strokes that are the main cause of long-term disability. According to statistics, 85% of people who have had a stroke need an intensive course of restoration of functional changes. Simply put, a third of patients who do not receive proper medical care after a stroke become disabled. To avoid this, you must immediately seek medical help and undergo a course of treatment and rehabilitation.
The first three months after the onset of a stroke, muscle tone increases in paretic (paralyzed) limbs, and slight muscle spasticity appears.
At this stage, it is not a pathology. However, the increase muscle tone leads to pronounced attacks of spasms in the muscles and the development of their contractures. For the complete recovery of the patient, it is necessary to remove muscle spasticity, otherwise he will not only lose his ability to work, but will also not be able to independently serve himself in everyday life.
Treatment of spasticity after a stroke
Recovery after a stroke is impossible without the cessation of muscle spasticity. At the first stage of rehabilitation, a number of exercises are used to reduce it: the patient is placed in various positions, thanks to which the spasms go away. These exercises can only be carried out by qualified medical personnel and in conjunction with physiotherapy, which includes paraffin heat treatment, application of applications and similar manipulations. Of great importance in the work to reduce muscle spasticity are manual therapy, gymnastics and medical massage.
In some cases, surgical treatment of muscle spasticity is prescribed; in rehabilitation after a stroke, this method of treatment is practically not used.
Three months after the stroke, muscle spasticity is unacceptable. It is at this time that muscle relaxants acquire the most important role in restoring the normal functioning of the limbs. With their help, you can reduce the tone of the striated muscles, reducing the motor activity of the muscles, up to the complete leveling of their contractions. Muscle relaxants are injected into the area of problem limbs. The need for treatment with drugs is determined only by the observing neuropathologist and only after three months have passed since the onset of the stroke.
Treatment with Dysport
One of the effective muscle relaxants used in our country is Dysport. Dysport is a botulinum toxin type A used to relieve muscle spasticity in patients who suffer from increased muscle tone without contracture after a stroke. In such patients, as a rule, muscle spasms are observed, accompanied by pain, as well as a violation of the motor function of the limbs.
Dysport is administered intramuscularly in several injections.

The clinical effect occurs only after some time: from several days to 2 weeks. The improvement lasts up to six months. In this case, the time of injection is of great importance. Treatment with dysport a year after a stroke will not lead to the same effect as early treatment. In this case, mild paresis may persist. Practical research dysport proved to be highly effective in the treatment of spasticity of the muscles of the hand after a stroke.
Dysport components can cause allergies. Side effects include pain at the injection site and minor skin rashes. With the introduction of Dysport for the first time, general weakness may be observed, with a second course of treatment, as a rule, these effects are not observed.
Dysport injections at the Three Sisters Center
Only qualified doctors with experience in diagnosing and treating the drug, as well as those who have undergone appropriate training, can prescribe and carry out treatment with Dysport. In no case should injections be given by an inexperienced doctor and without a preliminary examination. It's important to know that side effects can be avoided with the introduction of the minimum effective dose of the drug.
In the rehabilitation center "Three Sisters", Dysport is used in the treatment of patients undergoing a course of recovery after a stroke. Before the appointment of Dysport, patients of the rehabilitation center "Three Sisters" undergo a complete examination using the latest equipment. The specialists of the center have great experience treatment with this drug, regularly attend specialized training courses in Russia and abroad and know all the nuances of its use.
How to sign up for treatment
(8 800) 555 29 82 Free call within Russia
(+7 499) 755 77 75 Hotline
Previously, this word was unfamiliar to me. Spasticity resembles stiffness in very, very cold hands, when there is a desire to move your fingers, but it doesn’t work out. Plus, it also reduces and distorts them.
When my recovery from a stroke began, this condition was in fact in the whole body. Especially strong on the left side. I was almost completely paralyzed, but I still managed to make small movements. They turned out like in condensed milk. Tight, clumsy and very slow. In the hands, fingers, tension was constantly present. It did not pass for a minute, even in a calm state and did not allow to make normal movements. Hands involuntarily assumed an unnatural position. The left one was retracted away from the body. The right one was bent at the elbow and pulled up to the chest. I was very tired physically and mentally from the fact that I could not relax. Only in the prone position was it easier. But as soon as he sat down, the muscles of the body and limbs immediately tensed, as if abnormal. I quickly got tired again from excessive stress. It turned out to sit for one or two minutes and the forces ended.
The spasticity made it impossible to make subtle and precise movements. For example, if a cup of water was handed to me, I could not take it. Didn't "hit" it, missed it. When they put the cup into my hand, I could not hold it and clasp it with my fingers. They didn't shrink. At the same time, the tension in the hand was unreal. All this rigmarole was wildly exhausting. Removing spasticity in all limbs at once is not a realistic task. It's painfully big. And we, as always, broke a difficult task into simple fragments that became doable. We decided to divide the treatment of spasticity into pieces:
SPASTIC HANDS.
SPASTICATION OF THE LEGS.
It has become easier. In the process of training, I noticed that the reduction in spasticity in the left hand was accompanied by a slight relief in the right and in the legs. The connection is not significant, but noticeable. We did exercises and massages evenly for both left and right limbs. Although the spasticity was much stronger in the left side of the body. Over time, everything evened out. This approach turned out to be correct.
To remove spasticity turned out to be a complex of gymnastics and massages.
EXTREMELY IMPORTANT!
Start with minimal movements.
Do not give heavy loads during exercise.
Do the minimum number of repetitions.
Do not do active and strong massage. Only light touches.
Do not add or increase muscle tone.
Learn to relax your muscles and relieve tension in them.
Do not do gymnastics to relieve spasticity when tired.
Practice only in the morning.
While recovering from a stroke, I got used to the fact that there are no simple tasks. But the removal of the spasticity turned out to be an extremely difficult job. The point is the contradiction of the tasks performed. After a stroke, I needed to restore the strength of the muscles of the whole body. That is a lot and hard work. But at the same time it is necessary to treat spasticity. And for this load and endurance training, a hindrance. It turns out the first excludes the second. We solved this puzzle by alternating classes. One day: massage + gymnastics to relieve spasticity + exercises to restore balance and coordination. This does not require a lot of strength, the load is not great. The next day: strength exercises + endurance. And so on in turn.
AT this moment the splint was removed. There are leftovers, but they do not interfere. Freedom and ease returned to movement. The tension is gone. Muscle pain and fatigue are gone. I began to spend less energy on movement. This made it possible to smoothly increase the load on morning exercises.
In order for recovery after a stroke to give good results, you have to follow this regimen. Gradually I gain strength and increase endurance. Now I can do classes in one day. In the morning I do exercises with strength exercises. In the afternoon, gymnastics and massages to relieve spasticity + exercises for balance and coordination. Half a day, between classes, is enough to relax.
Exercises to relieve spasticity in:
SPASTIC HANDS.
For citation: Shirokov E.A. Stroke and muscle hypertonicity // BC. 2011. No. 15. S. 963
Acute cerebrovascular accident (ACV) is one of the most pressing problems of modern medicine. The number of stroke patients in the Russian Federation is increasing and currently exceeds 1 million people. The most significant consequences of cerebral vascular accidents are associated with movement disorders. Paresis and paralysis, impaired coordination of movements require complex rehabilitation measures aimed at restoring self-service skills and social adaptation. The restoration of lost motor functions is quite active during the first months after a brain stroke, and then the recovery rate decreases. As a rule, already the first weeks of the recovery period are characterized by a noticeable decrease in the degree of paresis, an increase in strength and range of motion. However, during this period, many patients have another problem - impaired muscle tone. Spasticity increases (C), which significantly limits the results of rehabilitation and often becomes an obstacle to the restoration of motor activity. The tone rises different muscles to varying degrees. This leads to the fact that the hand acquires a stable position with flexion in the elbow joint and the wrist joint. The leg with central paralysis, an important feature of which is hypertonicity, on the contrary, most often turns out to be unbent. Spasticity leads not only to the formation of stable pathological postures, but also contributes to pathological changes in the joints. As a rule, patients suffer from arthrosis and ankylosis, pain in the joints is no less than from paresis.
The development of C in case of damage to the structures of the central nervous system associated with a decrease in inhibitory effects on spinal motor neurons. A decrease in inhibitory effects on spinal structures is explained by a combined lesion of the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts of the brain, while an important role in the development of spasticity is assigned to damage to the cortico-reticulo-spinal tract. Under conditions of weakening of corticospinal stimuli, as a rule, dysfunction of the extrapyramidal system can also be observed. One of the leading mechanisms of C formation should be considered the disinhibition of the tonic stretch reflex. Secondary changes in muscles, tendons, and joints that occur during muscle hypertension increase movement disorders; therefore, resistance to passive movement depends not only on muscle tone disorders, but also on muscle changes, in which signs of atrophy can often be found. An isolated lesion of the pyramidal tract, as a rule, does not cause hypertonicity, but only leads to paresis. However, stroke usually causes damage not only to the pyramidal tract, but also to other structures, such as the cortico-reticulo-spinal tract, which leads to inevitable violations of muscle tone. If post-stroke paresis persists for a long time (several months or more), then structural changes in the segmental apparatus may occur. spinal cord(shortening of motor neuron dendrites and collateral sprouting of afferent fibers that make up the posterior roots), which contribute to a stable restructuring of the motor stereotype. This is facilitated by secondary changes in muscles, tendons and joints, which increase the resistance that occurs in the muscle when it is stretched. Knowledge of the pathogenesis of tonic disorders associated with stroke is necessary to understand the mechanisms of action of drugs, most of which have a so-called central mechanism of action.
It is possible to detect the first signs of growing muscular-tonic disorders already in the first hours after a stroke. Often they are characterized by a decrease in muscle tone. However, after a few days, spasticity becomes noticeable and increases along with the restoration of movement. The functional state of the muscles, muscle tone are assessed during a standard neurological examination of the patient, in the process of observing active movements, with passive changes in the position of body parts in space. Spasticity is characterized by an increase in muscle tone, which prevents the expansion of range of motion. Each time when performing the simplest movements, the patient has to overcome the resistance of tense muscles, which aggravates the picture of paresis or paralysis. A characteristic clinical sign of C is its change during the study - the tone increases with passive stretching of the muscle, and the increase in muscle resistance directly depends on the speed of passive movement. A frequent sign that reveals dystonia is uneven muscle tone during flexion and extension of the limb - the "jackknife" phenomenon. The degree of muscle tone disorders can change significantly during the day, under the influence of external and internal factors (weather, emotional state of the patient, ambient temperature). Patients who have had a stroke are characterized by a change in tone depending on the position of the limb, physical activity, its nature and intensity. Hypertonicity can delay recovery after a stroke, since with severe muscular dystonia, the patient's daily activity is limited to the bed: with any attempt to go to vertical position- persistent muscle tension prevents movement and forces the patient to return to a horizontal position again. There are other complications of the post-stroke period - limited mobility in the joints, arthrosis-arthritis and associated pain syndromes. Muscular dystonia has a significant impact on the statics of the spine, which in some cases becomes an independent problem (lumbalgia, thoracalgia, vertebrogenic radiculopathy). One of the most important questions that must be addressed in the management of a patient with post-stroke spasticity is the following: does high muscle tone impair the patient's functional capabilities or not? In general, the functionality of the limb in patients with post-stroke paresis of the limb is worse in the presence of severe spasticity than in its mild degree. At the same time, in some patients with a pronounced degree of paresis, spasticity in the leg muscles can facilitate standing and walking, and its decrease can lead to a deterioration in motor function and even falls. Before starting the correction of hypertonicity, it is necessary to determine the possibilities of treatment in this particular case (improvement of motor functions, reduction of painful spasms, facilitation of patient care, etc.) and discuss them with the patient and (or) his relatives. The possibilities of treatment are largely determined by the time since the onset of the disease and the degree of paresis, the presence of cognitive disorders. The shorter the time since the stroke that caused spastic paresis, the more likely improvement is. With a long duration of the disease, a significant improvement in motor functions is less likely, but care for the patient and discomfort caused by C can be greatly facilitated. The lower the degree of paresis in the limb, the more likely it is that treatment will improve motor functions. For clinical assessment of muscle tone and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for practical purposes, a modified Ashworth scale is used (Table 1).
The principles of correction of spasticity in the post-stroke period are based on the following provisions:
- pathologically increased muscle tone should be reduced in all cases to prevent irreversible changes in muscles and joints and accelerate the rehabilitation process;
- treatment should be started as early as possible, when the first signs of C appear;
- the duration of treatment is determined by the restoration of the patient's motor activity.
Drug therapy of muscular dystonia in stroke patients is based on the use of muscle relaxants. Before the appointment of muscle relaxants, it is necessary to establish how much an increase in muscle tone makes it difficult to move. In some cases (especially in the early recovery period), hypertonicity helps the patient to maintain support on the paretic limb - then the appointment of muscle relaxants can be delayed. However, this feature, as a rule, requires attention for a short period of time - during the first attempts of the patient to restore walking skills. In the future, a decrease in muscle tone plays a more important role in complex rehabilitation programs, since it allows you to expand the range of motion.
Most often, tolperisone is used to treat spastic syndromes. In its chemical structure, the drug is close to lidocaine. The action of the drug is based on the blockade of polysynaptic spinal reflexes. In addition, the drug has a central anticholinergic effect, has antispasmodic and moderate vasodilating activity. Tolperisone reduces increased muscle tone and muscle rigidity in spastic paresis, improves voluntary active movements, normalizes peripheral circulation, has a membrane-stabilizing, local anesthetic effect. Its use in adequate doses leads to increased local blood circulation. The main contraindication to the use is myasthenia gravis and intolerance to lidocaine. Usually the beginning of treatment falls on the 2-3rd week of a stroke - the period of activation of the patient. When the first signs of spasticity appear, 50-100 mg of the drug is prescribed per day, which in most cases facilitates movement. In later periods of the disease, with the formation of persistent spastic paresis, higher doses of muscle relaxants are also required. AT severe cases increasing spasticity is used intramuscular injection of the drug 100 mg 2 times a day. Tablets of 50 and 150 mg allow you to act in a wide range of therapeutic doses to achieve the desired effect. The vasodilating effect of tolperisone may be useful in severe atherosclerotic changes in the vessels of the lower extremities. The drug is well combined with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is important to note that the drug does not cause general muscle weakness. Tolperisone does not have a sedative effect.
To correct spasticity of various origins, other agents are also used: tizanidine, baclofen, dantrolene and benzodiazepines. The basis for the use of these antispastic drugs (or muscle relaxants) are the results of double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trials that have shown the safety and efficacy of these drugs. An analysis of studies comparing the use of various antispastic agents in a variety of neurological diseases accompanied by spasticity showed that tizanidine, baclofen and diazepam are approximately equally able to reduce spasticity.
In stroke patients with local spasticity in paretic muscles, botulinum toxin type A or botulinum toxin can be used. The action of botulinum toxin when administered intramuscularly is caused by blocking the neuromuscular transmission. The clinical effect after injection of botulinum toxin is noted after a few days and persists for 2-6 months, after which a second injection may be required. The best results are noted when using botulinum toxin in early dates(up to a year) from the moment of illness and with a mild degree of limb paresis. The use of botulinum toxin can be especially effective in cases where there is foot deformity caused by spasticity of the posterior calf muscles, or high tone flexor muscles of the wrist and fingers, impairing the motor function of the paretic hand. Repeated injections of botulinum toxin in some patients give a less significant effect, which is associated with the formation of antibodies to botulinum toxin and blocking its action. The limitation of the widespread use of botulinum toxin in clinical practice is largely due to the high cost of the drug.
Treatment with muscle relaxants begins with a minimum dose, then it is slowly increased to achieve the effect. Antispastic agents are usually not combined.
Surgical benefits for post-stroke spasticity are also possible. Surgery to reduce spasticity is possible at four levels - on the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves and muscles. Brain surgery includes electrocoagulation of the globus pallidus, ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus or cerebellum and implantation of a stimulator on the surface of the cerebellum. A longitudinal cone incision (longitudinal myelotomy) may be performed on the spinal cord to break the reflex arc between the anterior and posterior horns of the spinal cord. The operation is used for spasticity of the lower extremities, it is technically complex, associated with a high risk of complications, and therefore is rarely used. A significant part of surgical operations in patients with spasticity of various origins is performed on the muscles or their tendons. With the development of contracture, surgical intervention on the muscles or their tendons is often the only method of treatment for spasticity.
So, drug correction of muscle dystonia is carried out mainly with muscle relaxants, but in necessary cases, to reduce muscle tone, it is possible to use representatives of other drug groups acting on different levels pathological process. In each case, the treatment regimen and doses of drugs are determined individually.
It should be noted that the correction of muscle-tonic disorders is achieved by complex treatment, which includes properly organized and systematic physical therapy, massage, reflexology. Several types of exercise are usually recommended for stroke patients. The so-called general tonic and breathing exercises(helping improve general condition body), exercises to improve coordination and balance, to restore the strength of paralyzed muscles, as well as techniques to reduce muscle tone. Along with therapeutic exercises laying or treatment with a position is also used, in which the patient is laid in bed in a special way so as to create best conditions to restore the function of his arm and leg.
Literature
1. Gusev EI. The problem of stroke in Russia. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry. S.S. Korsakova (STROKE supplement to the journal). 2003; 9:3-7.
2. Parfenov V.A. Spasticity in the book: The use of Botox (botulinum toxin type A) in clinical practice: a guide for physicians. Ed. O.R. Orlova, N.N. Yakhno. - M.: Catalogue, 2001 - p. 108-123.
3. Formisano R., Pantano P., Buzzi M.G. et al. Late motor recovery is influenced by muscle tone changes after stroke // Arch Phys Med Rehabil. - 2005; 86:308-11.
4. Shirokov E.A. Sirdalud in the complex therapy of chronic pain syndromes//BC, 2006; 4:240-242.
5. Coward D.M. Tizanidine: Neuropharmacology and mechanism of action. //Neurology. 1994;11(9): S6-S11.
6. Hutchinson D.R. Tizadinine with modified release (review).//RMJ, 2007;12: 1-4.
7. Kadykov A.S. Rehabilitation after a stroke. M.: Miklosh Publishing House. - 176 p.
8. Gelber D. A., Good D. C., Dromerick A. et al. Open-Label Dose-Titration Safety and Efficacy Study of Tizanidine Hydrochloride in the Treatment of Spasticity Associated With Chronic Stroke // Stroke. 2001; 32:2127-31.
9. Kamchatnov P.R. Spasticity — modern approaches to therapy. http://www.medlinks.ru/article.php?sid=20428
10. Bakheit A.M., Thilmann A.F., Ward A.B. et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study to compare the efficacy and safety of three doses of botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) with placebo in upper limb spasticity after stroke // Stroke. 2000; 31:2402-06.
11. Francisco G.F., Boake C. Improvement in walking speed in poststroke spastic hemiplegia after intrathecal baclofen therapy: a preliminary study // Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 84:1194-9.
12. Ward A.B. A summary of spasticity management - a treatment algorithm // Eur. J. Neurol. 2002; 9(1): 48-52.
24.06.2016
Spasticity is a syndrome that develops as a result of various diseases. This condition is due to the fact that certain muscle groups in humans are in a state of constant tension. The tone increases when you try to strain the muscles and prevents you from making a passive movement.
Spasticity of the extremities occurs as a result of damage to the upper motor neurons, as a result of which tonic reflexes are enhanced, including in the tendon region, and the conduction of nerve fibers is disturbed. This disease is not an independent syndrome, but occurs as a result of other diseases.
What pathologies cause spasticity? The cause of increased tone can be:
- strokes;
- traumatic brain injury and spinal injury;
- hypoxia of brain cells due to various diseases;
- phenylketonuria;
- meningitis or encephalitis of the brain;
- often such a syndrome occurs with cerebral palsy or multiple sclerosis.
Symptoms
Muscle spasticity may be accompanied by involuntary twitching of the limbs, sharp contractions. Common symptoms include transient pain that precedes the onset of spasm, a feeling of loss of dexterity, chronic fatigue and malaise. A person feels weakness in the arms and legs, or vice versa, increased muscle stiffness, which prevents the performance of a particular movement.
If spasms, sharp twitches can be removed with the help of medications, then weakness is a persistent symptom.
Spasticity of the lower extremities in a mild form is characterized by "clogging" of the muscles, chronic fatigue. If the syndrome progresses, then it becomes difficult for a person to unbend and bend his toes, pull his legs towards him, bending them at the knees.
Spasticity of the upper extremities is inherent in the fact that it is difficult for the patient to bend and straighten the fingers, it becomes difficult to straighten the arms. In a more severe form of the hand, the hands are constantly gathered into a fist, the elbow and shoulder joints are in a bent position all the time. In more severe forms of the disease, the joints are fixed in a non-physiological position for them.
Treatment
For the treatment of spasticity, doctors recommend combining drug and non-drug methods. The therapist or neurologist begins treatment with the minimum dose of the drug, gradually increasing it until the desired effect is achieved.
A drug baclofen, is a centrally acting muscle relaxant, it effectively relaxes the muscles, acting for 4-6 hours. Although gabapentin is and is an antiepileptic drug, it also eliminates convulsive syndrome, leading to a decrease in tension in muscle fibers.
diazepam, clonazepam also prescribed for patients suffering from spasticity. In addition to the muscle relaxant effect, they also have anti-anxiety and sedative effects, reduce nervous excitability.
Physiotherapy methods
Gymnastics, medical massage, reflexology are also effective means treatment of this disease. Special exercises performed with the participation of both affected limbs at a slow and medium pace promote relaxation and help restore lost motor activity.
![]() But if physical exercise do not lead to the desired result, but only increase spasticity, then classes physical therapy should be stopped. Orthopedic devices, bandaging of limbs, exposure to affected areas of the body with low-frequency electric current- all these methods can alleviate the patient's condition.
But if physical exercise do not lead to the desired result, but only increase spasticity, then classes physical therapy should be stopped. Orthopedic devices, bandaging of limbs, exposure to affected areas of the body with low-frequency electric current- all these methods can alleviate the patient's condition.
Splinting, bandaging of hands and feet is recommended for severe muscle hypertonicity. The fact is that a long stay in a stretched position helps to reduce their tone. The affected limb is immobilized and fixed in an extended position for a period of time from 1 to 3 hours a day.
Procedures therapeutic massage help to strengthen the body, relax spasmodic muscles, improve the patient's condition. Botox injections, together with physical therapy exercises, can normalize muscle tone for a long time or reduce the manifestations of spasticity.
Botulinum toxin type A is administered intramuscularly, where it blocks neuromuscular transmission, temporarily relaxing tense areas. Lasting results are achieved approximately 3 weeks after injections and last up to 3 months.
- People suffering from spastic limbs should remember that tight-fitting clothing, tight shoes, inflammation of the skin, hypothermia, drinking coffee or alcohol - all this can increase muscle activity.
- A person should regularly visit a doctor so that the specialist makes timely adjustments to the treatment depending on the patient's condition.
- If in parallel with taking drugs that reduce hypertension, you practice therapeutic exercises, then you should start the exercises no earlier than an hour after taking the appropriate medications.
- Spasticity is a condition that requires competent treatment. An integrated approach to the treatment of this disease contributes to the weakening unpleasant symptoms improves the quality of life, increases physical activity.
Muscle spasticity and its treatment updated: June 24, 2016 by: author

Stroke Probability Calculator
Is there a risk of stroke?
Prevention
Age
1. Increased (more than 140) blood pressure:
3. Smoking and alcohol:
4. Heart disease:
5. Passage of medical examination and diagnostic MRI:
Total: 0%
Stroke is a rather dangerous disease that affects people far from only the senile age, but also the middle and even very young.
A stroke is an emergency situation that requires immediate help. It often ends in disability, in many cases even death. In addition to blockage of a blood vessel in the ischemic type, a hemorrhage in the brain against the background of high blood pressure, in other words, a hemorrhagic stroke, can also cause an attack.
Risk factors
A number of factors increase the chance of having a stroke. For example, genes or age are not always to blame, although after 60 years the threat increases significantly. However, everyone can do something to prevent it.
1. Avoid hypertension
Increased arterial pressure is a major risk factor for stroke. Insidious hypertension does not show symptoms on initial stage. Therefore, patients notice it late. It is important to have your blood pressure checked regularly and take medications for elevated levels.
2. Quit smoking
Nicotine constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. A smoker is twice as likely to have a stroke than a non-smoker. However, there is good news: those who quit smoking significantly reduce this risk.
3. With excess body weight: lose weight
Obesity is an important factor in the development of cerebral infarction. Obese people should think about a weight loss program: eat less and better, add physical activity. Older people should talk to their doctor about the extent to which they benefit from weight loss.
4. Keep cholesterol levels normal
Elevated levels of "bad" LDL cholesterol lead to deposits in the vessels of plaques and embolism. What should be the values? Everyone should find out individually with a doctor. Since the limits depend, for example, on the presence of concomitant diseases. In addition, high values of "good" HDL cholesterol are considered positive. healthy image life, especially balanced diet and more exercise may positively affect cholesterol levels.
5. Eat healthy food
Useful for blood vessels is a diet that is commonly known as "Mediterranean". That is: lots of fruits and vegetables, nuts, olive oil instead of cooking oil, less sausage and meat, and lots of fish. Good news for foodies: you can afford to deviate from the rules for one day. It is important to eat right in general.
6. Moderate alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption increases the death of stroke-affected brain cells, which is unacceptable. Complete abstinence is not required. A glass of red wine a day is even helpful.
7. Move actively
Movement is sometimes the best thing you can do for your health in order to lose weight, normalize blood pressure and maintain the elasticity of blood vessels. Ideal for this endurance exercise, such as swimming or brisk walking. The duration and intensity depend on the personal physical training. Important note A: Untrained over 35 years of age should be initially examined by a doctor before starting to play sports.
8. Listen to the rhythm of the heart
A number of heart conditions contribute to the likelihood of a stroke. These include atrial fibrillation, birth defects, and other rhythm disturbances. Possible early signs of heart problems should not be ignored under any circumstances.
9. Control your blood sugar
People with diabetes are twice as likely to have a cerebral infarction than the rest of the population. The reason is that elevated glucose levels can damage blood vessels and promote plaque buildup. In addition, diabetic patients often have other risk factors for stroke, such as hypertension or too high blood lipids. Therefore, diabetic patients should take care of the regulation of sugar levels.
10. Avoid stress
Sometimes stress has nothing wrong, it can even motivate. However, prolonged stress can increase blood pressure and susceptibility to disease. It can indirectly cause a stroke. There is no panacea for chronic stress. Think about what is best for your psyche: sports, an interesting hobby, or perhaps relaxation exercises.
Removing spasticity after a stroke proved extremely difficult. The point is the contradiction. We stubbornly restored strength and endurance. Did it with special exercises With high load and lots of repetition.
For the treatment of spasticity, this is a hindrance and harm. When removing spasticity, a relaxing massage and light movements in the exercises are needed. In order to continue recovery after a stroke, it is necessary to conduct mutually exclusive classes. But we came up with a simple solution. Make two groups of exercises.
First: to restore strength and stamina. Second to treat spasticity, restore balance and coordination. The decision turned out to be very correct. True, we didn’t reach it right away and for some time did exercises to relieve spasticity along with exercises for strength and endurance. In time, they noticed that spasticity increases from active exercises.
What is spasticity
Spasticity appears in stiffness. Impossible to make a quick or abrupt movement. Constantly tense muscles block freedom. Feeling like you are a very rusty Terminator))).
Stress leads to fatigue.
Stroke recovery can be effectively blocked by spasticity. It is difficult to restore skills when the limbs seem to be bound with elastic bands and are always in a tense, unnatural position. To relieve spasticity after a stroke, we use elementary exercises. The main thing is to do them easily, without stress.
Muscle spasticity is an involuntary contraction, convulsions or spasm due to a violation of the conduction of nerve impulses after an injury to the spinal cord and brain.
More often this condition manifests itself at night, but it can also significantly complicate life during the day.
Mechanism of spasticity formation
The main reason for the formation of seizures, experts call the imbalance of the inhibitory effect of the motor elements of the cerebral cortex on the cells in the structure of the spinal cord.
The logical result is the disinhibition of the tonic reflex - muscle spasticity is formed in the injured limbs of a person.
In a normal state, a person does not have to think about the sequence of phenomena produced in the muscles: which of them first need to be reduced, then relaxed - our brain has brought such activity to automatism.
After a stroke or injury, the death of cellular elements responsible for special inhibitory impulses in the motor neurons of the brain and spinal cord occurs. Reflex arc: limb - spinal cord - brain ceases to be unified system- there is a lack of coordination.
Spasms do not form immediately - for weeks, and even months. Leads to significant secondary changes in muscles and joints - increases the negative impact of paresis on the motor system.
The severity of spasticity of the limbs
The first signs of the beginning of the formation of muscle spasticity are observed on the first day after the injury, and subsequently tend to increase.
The degree of severity can change under the adverse influence of negative factors, for example:
- with a change in emotional mood - a person has a tendency to depressive states;
- when weather conditions change - fluctuations in temperature or light parameters;
- with excessive physical overload caused by the early physical activity of the victim, contrary to the recommendations of the doctor.
With an increase in the intensity of the load on muscle fibers in the limbs, there is a difficulty in their motor activity, there are symptoms of pain in them, of varying severity.
According to the severity of spasticity, the following forms are distinguished:

Spasticity of the legs in a mild form is manifested by rapid fatigue of the muscles of the legs, a feeling of "clogged muscles", from physical activity, while walking becomes easier on the heel, then it becomes difficult to pull the toes towards you and straighten it at the knee.
In a severe form of spasm: one or two legs are fixed in a bent knee or hip joints and the foot turns inward or outward. When walking without special shoes or, deformities or contractures may occur. 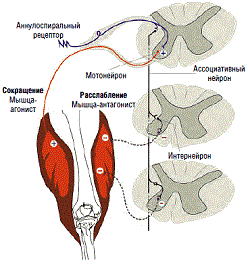
Manifestation of hand spasticity in a mild form: extension is difficult
fingers and straightening of the arm in the elbow joint, a sign of a severe form is bent at the elbow and shoulder joints, while the hand is clenched into a fist.
If spasticity is present for a long time without treatment, contracture develops, that is, the joint is not fixed in a physiological state for the body.
In the future, the spasm will only have a negative impact on the conduct of recovery activities. In addition to the limbs, it will worsen recovery in the spine: an increase in muscle tone causes pain in the back - symptoms of vertebrogenic sciatica.
Experts note: than before adequate treatment with modern drugs was started, and also, the less the severity of spasticity, the better the prognosis of rehabilitation measures.
Even if the symptoms are significantly pronounced, and the treatment of seizures for certain reasons began at a later time period - a decrease in spasticity significantly improves general well-being.
How to treat spasticity with different methods
The most important requirement for treatment is its maximum possible painlessness, since the pain is multiplied by spasticity.
An important point is also the control over the activity of the pelvic organs - the prevention of inflammatory manifestations in them, as well as the timely implementation of measures to prevent the occurrence of contractures and.
 A complex of modern treatment for getting rid of spasticity:
A complex of modern treatment for getting rid of spasticity:
- drug tactics (mydocalm, baclofen);
- methods;
- orthotics;
- surgical correction.
The complex of treatment is selected only individually, in direct proportion to the localization of the focus and the severity of spasticity. It is necessary to take into account the technical capabilities of the medical institution.
Spasticity after a stroke or brain injury necessarily requires medication. Treatment should be carried out in stages gradual increase therapeutic dose of medication, possibly by replacing the drug.
 There are currently two subgroups in demand:
There are currently two subgroups in demand:
- Drugs with a central mechanism of action on the negative focus - inhibition of the reflex.
- Peripheral drugs - significantly reduce the stretch reflex at the level of the elements of the spinal cord: muscle relaxants.
Like other subgroups of even the most modern drugs, the above have their own contraindications, so only a highly qualified neurologist should deal with their appointment.
Orthotics and plaster
Treatment of spasticity by prolonged laying of the limbs of a person, in a position where the muscles are optimally stretched, and the tonic reflex activity is reduced, is called orthotics by specialists. It helps to reduce hypertonicity in the limbs - pathological symptoms can be reduced many times over.
With severe spasticity, even the imposition of a special plaster splint or splint is recommended to prevent the development of contracture. It is the tire that fixes the limb in the most acceptable position - in which the muscle fibers are located in a stretched position.
Treatment with orthotics is carried out from one to two hours, in direct proportion to the sensations of a person - with increased pain, the procedure is completed.
Physiotherapy for muscle stiffness
- local use of cold - helps to reduce excessive reflexes and maximize the range of motion, improve muscle activity;
- local use of heat - perfectly contributes to a temporary decrease in tone. carried out with the help of ozocerite or paraffin applications, the course is at least twenty procedures;
- nerve endings - an excellent technique that allows you to achieve a maximum response in the affected areas, the duration of the treatment course is prescribed by a specialist.
exercise therapy development
 Treatment with the help of exercises aimed at optimal relaxation of the fibers in the muscles is a long-proven, well-established rehabilitation technique for the treatment of spasticity.
Treatment with the help of exercises aimed at optimal relaxation of the fibers in the muscles is a long-proven, well-established rehabilitation technique for the treatment of spasticity.
Dosed therapeutic stretching allows for a couple of hours to lower their tone, to maximize the range of motion in the affected limbs.
The kinesiotherapist knows that a decrease in tone will be observed only for a certain time, and therefore it must be effectively used for other complex exercises that were difficult due to spasticity.
Surgical intervention is determined by a specialist according to strictly individual indications, when conservative methods have already exhausted themselves, and there is no pronounced positive dynamics.
Removing spasticity is an important task. She interferes greatly Everyday life, takes away strength and constrains movement. This makes it difficult to restore lost skills and stamina. To fully carry out recovery after a stroke, it is necessary to cure spasticity. We do this in parallel with other tasks.
With an integrated approach and the beginning of therapeutic measures at the earliest possible stage, drug treatment - the normalization of muscle tone contributes to the maximum acceleration of the patient's recovery.
In the treatment, methods such as myostimulation, Botox, of course, showed themselves well. physiotherapy, medications (mydocalm, baclofen) and sparing surgery.
What is, causes of spasticity, prevention and treatment updated: November 21, 2017 by: author
